User Journey Scenario and Customer Journey Map
A user journey is a path a user may take to reach their goal when using a particular website/application.
User journeys are used in designing websites to identify the different ways to enable the user to achieve their goal as quickly and easily as possible.
User journeys map out every step to reach a goal
- User journeys are the step-by-step journey that a user takes to reach their goal. This journey will often consist of a number of website pages and decision points that carry the user from one step to another.
- The output is traditionally a flow diagram demonstrating each page and decision point throughout the entire process.
When to use user journeys?
User journeys work best when the product team wants to understand the entire experience from the user’s standpoint.
- It usually happens during design review sessions
- User journeys help the team to prioritize tasks per the user’s needs.
First, understand who is using your website
- In order to create realistic user journeys, it is important to first identify the users.
- Each user will have a task or goal they are trying to reach on the website, whether
it is purchasing a product, finding opening times or cancelling a direct debit in a bank.
Second, map out the easiest user journey
- Create a scenario and think of the user behavior based on their experience
- Once an understanding of existing user journeys is fully illustrated, website
designers can set out their recommended user journey - User journeys are critical in the design of new websites by highlighting the current issues and producing an ideal picture from a typical user’s perspective early in the process.
What are Customer Journey Maps?
- Customer journey maps are used to map the relationship between a customer and an organization over time and across all channels on which they interact with the business.
- CJM (customer journey map) is an effective tool for visualizing user interaction with a website, product, or service
- CJM help define the goals of users, their needs, barriers and problems that arise when navigating from the first interaction to the purchase.
- Maps also help identify points of contact and, what is really needed for UX, predict the approximate emotional state of users at each point.
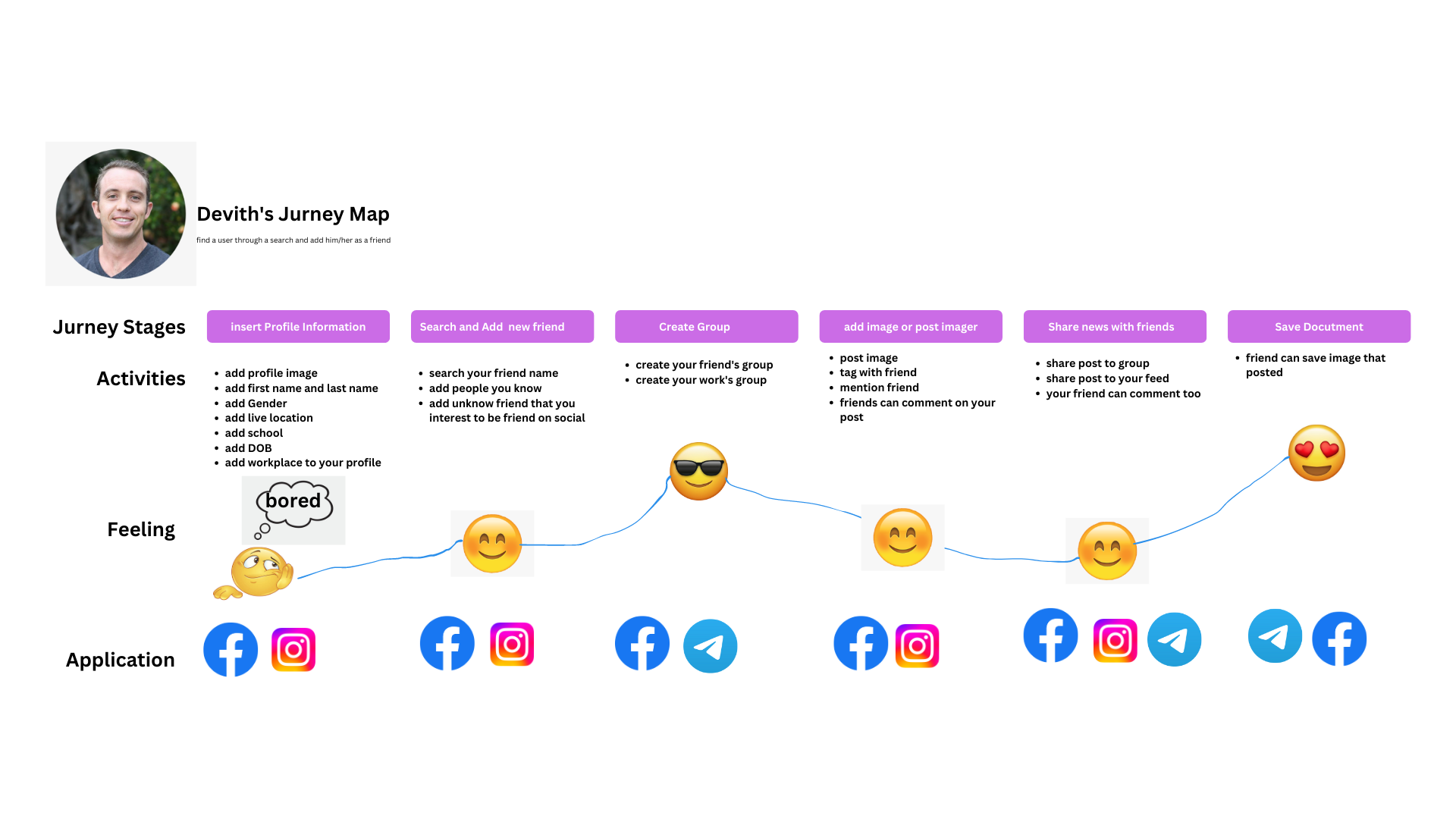
- CJM is a diagram showing all stages of a service consumption path from beginning to end.
- These maps should be detail-rich timelines that show the most important sub-tasks and events.
Barriers and problems that users may face in the process of moving to a purchase, they can be triggered by various reasons.
For example:
- Technical (incorrect operation of buttons or links, “dead ends” in the interface, impossibility of receiving feedback);
CJM should consist of:
- A timescale – a defined journey period (e.g., 1 week)
- Scenarios – the context and sequence of events in which a user/customer must achieve a goal (e.g., a user wants to buy a ticket on the phone), from first actions (recognition of a problem) to last actions (e.g., subscription renewal).
- Touchpoints – what customers do while interacting and how they do it.
- Channels – where they perform actions (e.g., Facebook).
- Thoughts and feelings -what the customer thinks
and feels at each touchpoint.
How to make Customer Journey Maps
To create a customer journey map, you can follow these steps:
- Define your Map’s Business Goal – Clarify who will use your map and what user experience it will address.
- Conduct Research – Use customer research to determine customer experiences at all touchpoints.
- Review Touchpoints and Channels – List customer touchpoints (e.g., pay a bill) and channels (e.g., online). Look for additional touchpoints or channels to include.
- Make an empathy map – Pinpoint what the customer does, thinks, feels, says, hears, etc. in a given situation. Then, determine his/her needs and how he/she feels throughout the experience.
- Sketch the Journey – Piece together everything (touchpoints, timescale, empathy map output, new ideas, etc.) however you like(e.g., a map).
- Share with Stakeholders – Ensure all stakeholders have your map, understand it and appreciate how its use will bring beneficial changes to customers and across the organization.
- Case study : Spotify Spotify is one of the world’s most popular audio streaming services. When Spotify wanted to improve the music-sharing experience for its customers, it hired a marketing firm to create a customer journey map. The goal of this customer journey map was to determine where music sharing features the best fit into the customer experience.
Category :
Tags :
Share this Article!