In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn how to install, configure, and customize Moodle. Discover the best practices on creating courses, adding users, and troubleshooting common issues.
Introduction to Moodle
Moodle is a popular learning management system used by educational institutions around the world. It provides a platform for teachers to create online courses with interactive content, including videos, quizzes, and assignments. With Moodle, teachers can engage their students anytime, anywhere, on any device.
System Requirements
Server requirements
- Linux, Windows, or macOS operating system
- Web server (Apache, Nginx, IIS)
- PHP 7.2 or later
Client requirements
- Modern web browsers (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari)
- Internet connection
Installation Process
|
Step 1: |
Download Moodle from https://download.moodle.org/ |
|
Step 2: |
Unzip the file and copy to your web server |
|
Step 3: |
Run the installation script |
|
Step 4: |
Follow the prompts and enter your configuration settings |
|
Step 5: |
Finish the installation and log in to Moodle |
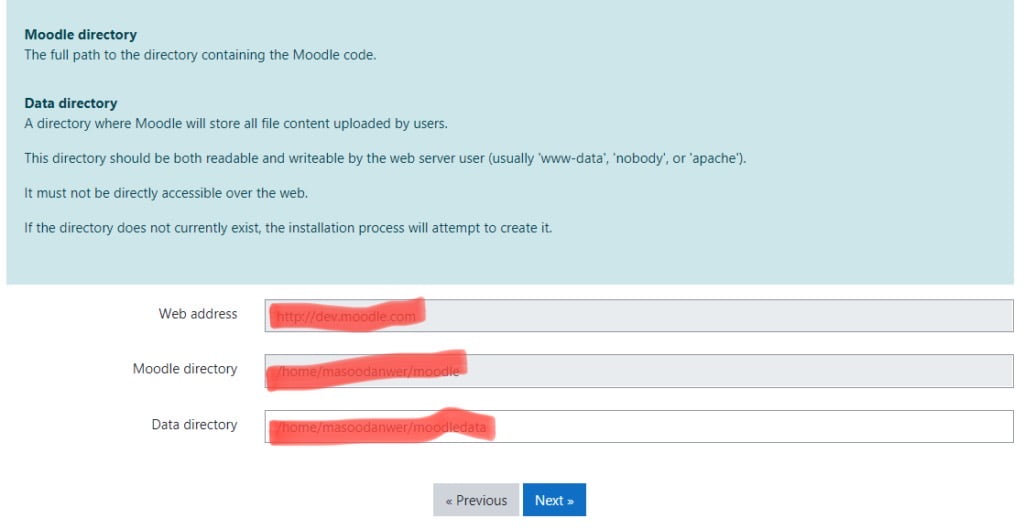
- Download and copy files into place.
Install Moodle on your own server (requires a web server with PHP and a database) by downloading one of the following packages or https://github.com/moodle/moodle and clone it to your computer.
check the command as below:
$ cd /path/to/your/webroot $ git clone git://git.moodle.org/moodle.git (1) $ cd moodle $ git branch -a (2) $ git branch --track MOODLE_401_STABLE origin/MOODLE_401_STABLE (3) $ git checkout MOODLE_401_STABLE (4)Clone it to C:/wamp/www (Wamp ) or C:\xampp\htdocs (Xampp).
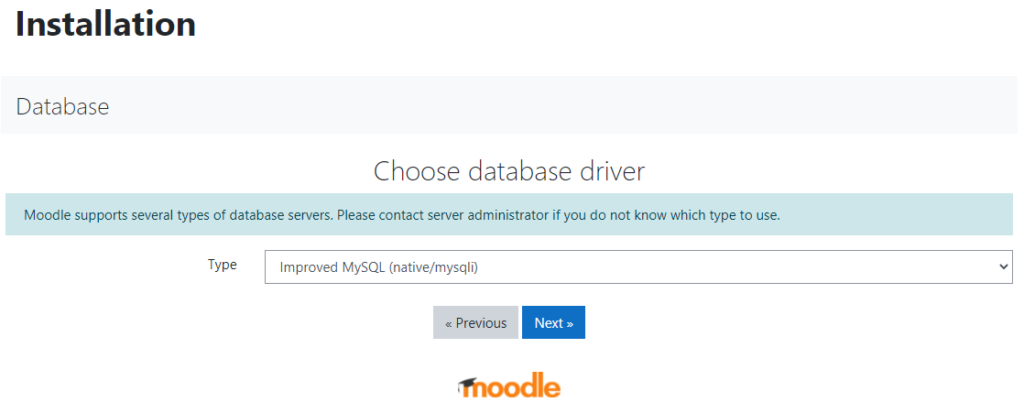
- Connect Moodle Project with Database
Open phpMyAdmin and create a database name.
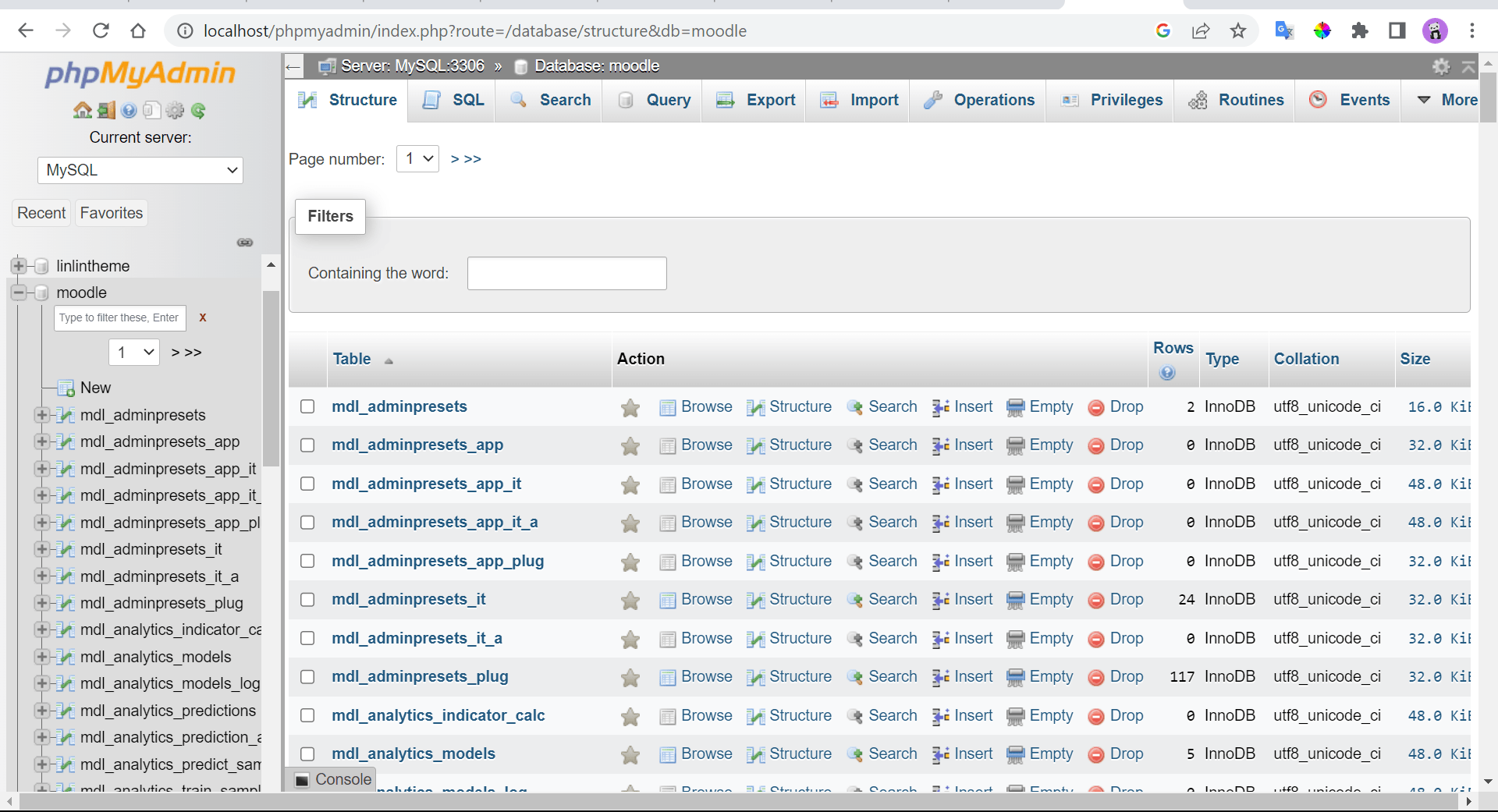
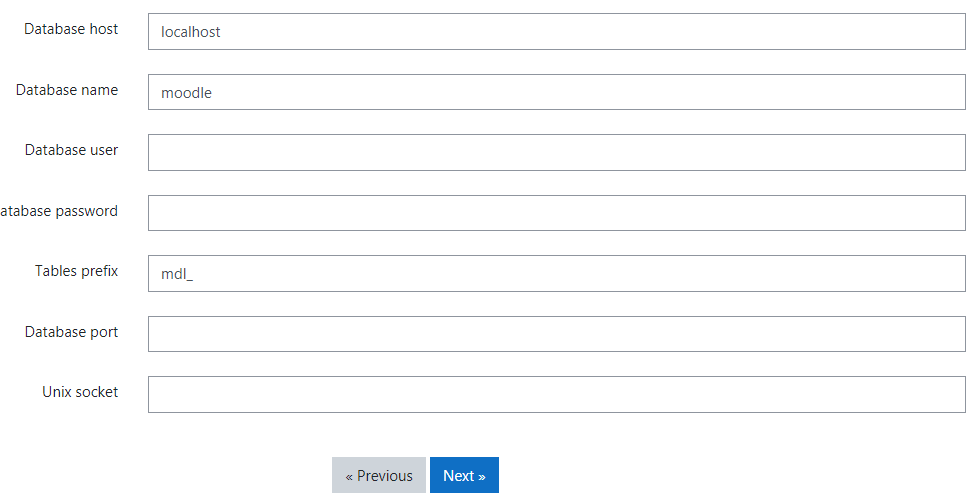
- Configuration
after creating the database name in phpMyAdmin was done.
Open this URL: http://localhost/moodle/ Then you need a complete DB port, database name, username, email, and password.
You can check moodle/config.php to view the project environment as dbname, port, etc.
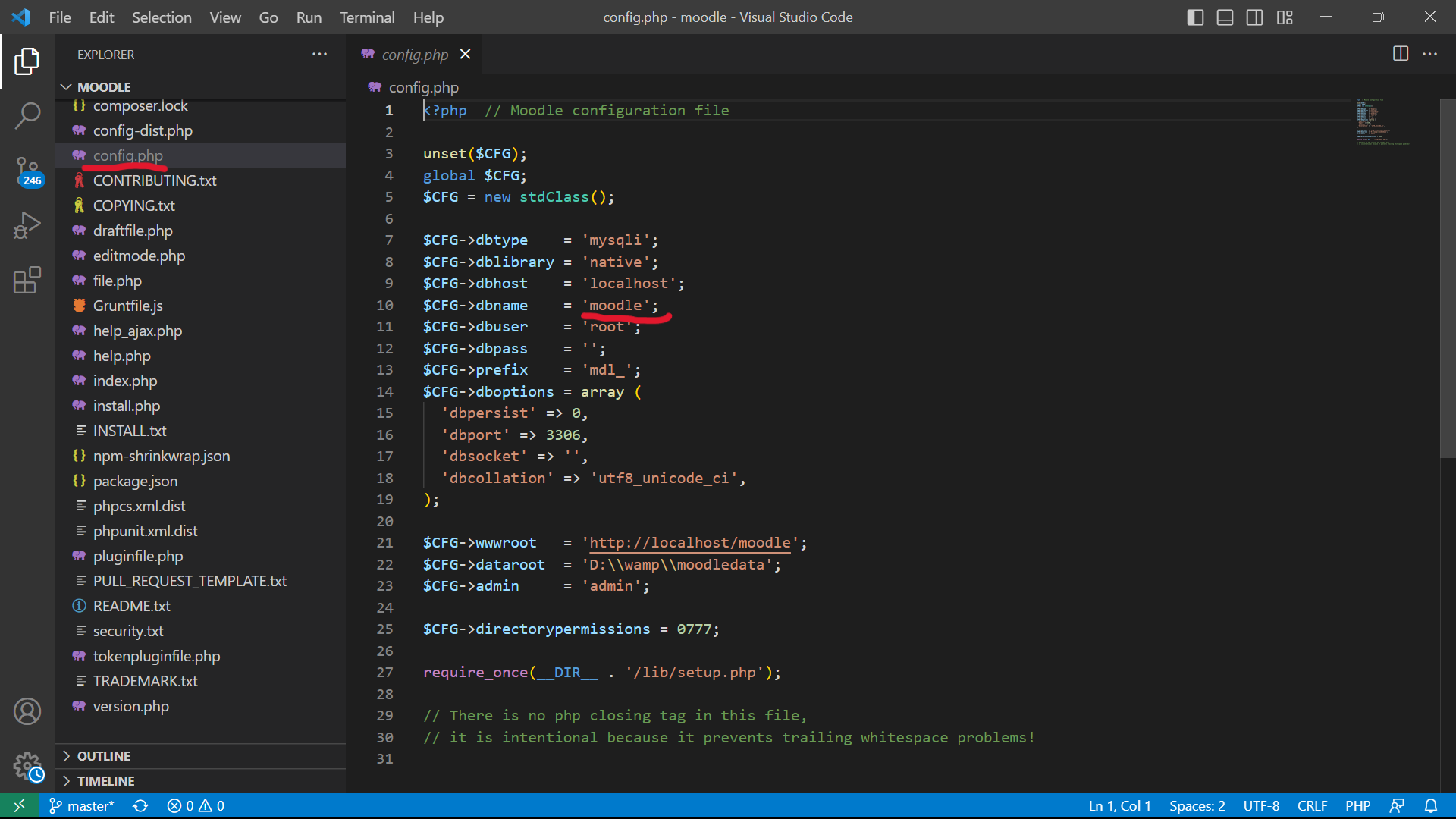
- Result
Configuration Settings
-
Site Settings: Set up site name, description, language, and timezone.
-
Security Settings: Set up user authentication, password policy, and account lockout.
-
Security Settings: Set up user authentication, password policy, and account lockout.
Adding Courses and Users
-
Create a Course: Design your course with engaging content and activities that boost learning outcomes.
-
Add Users to a Course: Enroll students, teachers, and other instructors to your course with ease.
Customizing Moodle
Moodle is highly customizable, allowing you to change the look and feel of your site with themes, and enhance its capabilities with plugins. You can also extend Moodle’s functionality with APIs, integrations, and custom code.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
-
Blank Pages
If Moodle pages appear blank, check PHP settings and memory limit. Disable third-party plugins and debug errors.
-
Installation Errors
If you encounter installation errors, verify your server meets Moodle’s requirements. Check installation logs for clues.
-
Login Issues
If users can’t log in, check authentication settings, user database, and login block settings. Run the diagnostics tool to diagnose errors.
Category :
Tags :
Share this Article!