HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages.
- HTML consists of a series of elements.
- HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content.
Example Explained
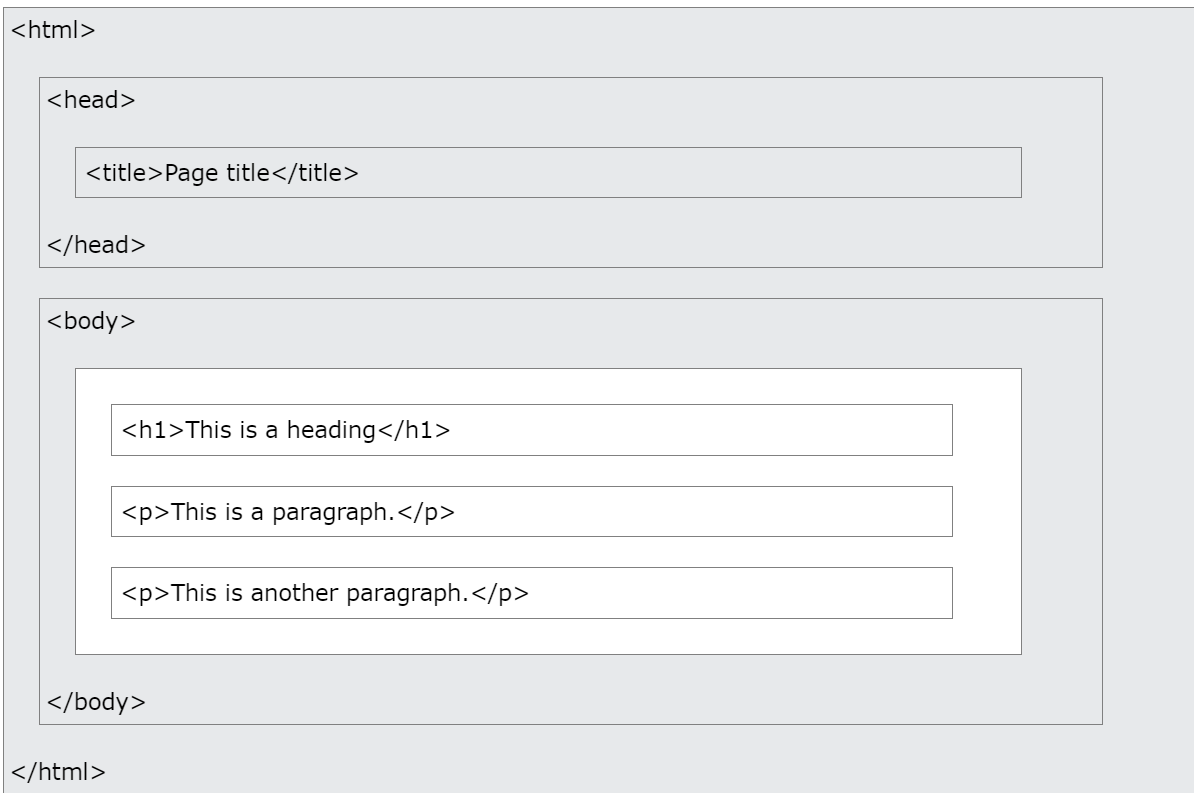
- The
<!DOCTYPE html>declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document - The
<html>element is the root element of an HTML page - The
<head>element contains meta information about the HTML page - The
<title>element specifies a title for the HTML page (which is shown in the browser’s title bar or in the page’s tab) - The
<body>element defines the document’s body, and is a container for all the visible contents, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc. - The
<h1>element defines a large heading - The
<p>element defines a paragraph
HTML Page Structure
Other Key Elements
| Element | Meaning | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| <b> | Bold | Highlight important information |
| <strong> | Strong | Similarly to bold, to highlight key text |
| <i> | Italic | To denote text |
| <em> | Emphasised Text | Usually used as image captions |
| <mark> | Marked Text | Highlight the background of the text |
| <small> | Small Text | To shrink the text |
| <strike> | Striked Out Text | To place a horizontal line across the text |
| <u> | Underlined Text | Used for links or text highlights |
| <ins> | Inserted Text | Displayed with an underline to show an inserted text |
| <sub> | Subscript Text | Typographical stylistic choice |
| <sup> | Superscript Text | Another typographical presentation style |
Let’s try it out. On a new line in the HTML editor, type the following HTML code:
<p>Welcome to <em>my</em> brand new website. This site will be my <strong>new<strong> home on the web.</p>
Category :
Share this Article!